Use our convenient online scheduler to book an appointment now.
If you’ve hurt your shoulder, there is a good chance that you may have suffered a labrum tear. The labrum is a cartilage ring of tissue around the socket of your shoulder to help stabilize the ball of the joint. A torn labrum can cause pain, weakness, reduced range of motion, and stiffness. If you have a labrum tear, arthroscopic surgery can be a treatment option. On the other hand, a torn labrum in the shoulder that isn’t causing symptoms usually doesn’t require surgical intervention.
If you come in for evaluation and you are having any of the above symptoms, the job of our team is to determine whether you have a labral tear and if it requires labrum surgery.
There are several types of labral tears:
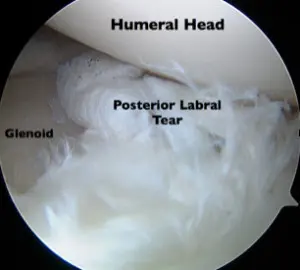
- Those caused by significant trauma, such as a dislocation
- Those caused by repetitive microtrauma, like throwing a ball
- Those caused by normal labral degeneration that occurs with age
Since they usually are not symptomatic, degenerative labral tears are often treated without surgery. However, labral tears caused by trauma, whether a single violent event or multiple smaller (microtrauma) events, usually require surgical treatment. Dr Aaron Carter, Shoulder and Sports Medicine Specialist reviews common questions about Labral Tear Surgeries.
What Causes a Labrum Tear?
Several different causes can contribute to a torn labrum in the shoulder. They can happen from repetitive overhead motions in sports, traumatic events such as a fall or pull to the arm, and general wear and tear in the shoulder that occurs with aging.
When Is Labral Tear Shoulder Surgery Recommended?
Shoulder-torn labrum surgeries are recommended in patients who have exhausted nonoperative treatment, typically involving anti-inflammatories, therapy, and sometimes injections. For patients complaining of pain or discomfort, the injury frequently concerns the labrum. If so, these patients are often considered for surgery. Patients should always consult with their doctor or orthopedic specialist to determine whether surgical intervention is necessary.
<span
Which Torn Labrum Shoulder Surgery Option Is Right for You?
Depending on the location and extent of the injury, your surgeon may perform either debridement or a repair. Both options are minimally invasive outpatient procedures with high success rates.
Labral Tear Shoulder Surgery: Debridement
Some labral tears cause symptoms because the torn labral tissue irritates the capsule or adjacent lining of the joint. In other cases, the torn tissue catches in the joint when the shoulder moves.
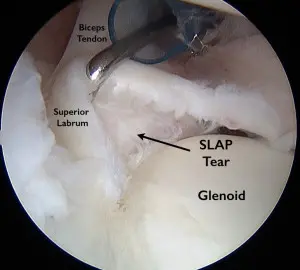
If the shoulder tissue is significantly damaged or the bulk of the labrum is attached to the glenoid (socket) and the cause of the symptoms is just a flap or small free piece of the labrum, debridement is typically the most effective shoulder labrum surgery option.
In a labrum debridement surgery, torn labral tissue is removed arthroscopically, where the surgeon will make small incisions around the shoulder. The surgeon will then go to the area where the labrum tissue is fraying. When it cannot be repaired, a surgeon will trim away the frayed edges, which may be pain generators in the shoulder.
In many cases, the bulk of the labrum remains attached to the glenoid, as do the shoulder ligaments. Consequently, the shoulder maintains stability and has full function.
What Is Recovery Like After Debridement?
Since the tissue is not repaired or reattached to the glenoid, there is no need to protect it after surgery. Most patients use an arm sling for comfort for a few days. Physical therapy can start immediately, and there are no restrictions on activity other than those due to your pain.
The recovery period for shoulder debridement is generally much shorter than for other torn labrum surgeries. Most patients see improvement in their pre-operative symptoms within one to two months and fully recover within three to six months.
Labral Tear Shoulder Surgery: Repair
When strong labral tissue separates from the glenoid, the preferred surgical solution is usually a labral repair.
This is almost always the case in those who have sustained traumatic instability events (dislocations or subluxations). Athletes who perform overhead motions (like swimmers, throwers, or volleyball players) and sustain labral tear shoulder injuries also often require surgical repair. However, on occasion, different types of surgery may be required.
How Is Labral Repair Surgery Performed?
Labral repair surgery can be performed either arthroscopically or as open surgery using larger incisions. Labral repair procedures are often performed arthroscopically. Only in unique cases, primarily those with a significant injury to the humerus (upper arm bone) and/or glenoid, will we perform an open labral repair surgery.
Repairing a torn labrum arthroscopically is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure. The surgeons will make small incisions around the shoulder and enter the joint to address the labrum tear. The surgeon will reattach the torn labrum securely to the glenoid using suture anchors. Patients can go home the same day.
The surgery allows us to:
- Address any issues like biceps tendonitis, subacromial bursitis, or loose bodies without a second procedure.
- Remove any torn flaps of the labrum.
- Mobilize the labrum if needed.
- Promote blood flow at the glenoid attachment site to support healing.
The postoperative treatment requires the use of a sling for support with or without an ice sleeve. The amount of time in a sling is typically determined by the type of labral surgery performed.
If you have further questions or want to meet one of our orthopedic specialists, request an appointment or call us at (571) 250-5660.
Join our Mailing List
TCO provides patients with orthopedic problems the trusted resources and patient-centered advice they need to “Feel Better. Move Better. Be Better.”
© 2024 Town Center Orthopaedics | All Rights Reserved


